Spark 3.0 推出了 Catalog Plugin 特性。在 Release Note 里面位于 Highlight 部分。我们这篇文章就来介绍一下 Catalog Plugin 机制。

Catalog Plugin 的设计文章在 Google Doc 上: SPIP: Spark API for Table Metadata。本文部分参考于这篇设计文档。
1. 背景
DataSourceV2 是 Spark 2.x 新推出的 API,主要目的是用来和外部数据存储进行集成,比如数据读写。但是这里缺少关键的一环:对表的元数据进行操作,比如创建、修改、删除表等。
SparkSQL 和 DataFrame 操作都支持 CTAS (Create Table AS Select) 用来创建一个表并向该表写入数据,注意这里是一个操作。缺少创建目标表的 API,CTAS 的实际行为将完全取决于 DataSourceV2 的实现。比如写表失败,表可能被保存也可能被删除。并且在某些 SaveMode 下,我们无法区分 CTAS 和普通的写操作,那么很有可能在 Append 模式下写表的时候会因为表被删除而失败。最后一点,Spark 没有一种机制用来设置由 CTAS 创建的表,比如分区。
除此之外,数据工程师也希望类似 CTAS 的 high-level 操作在数据源上面进行操作的时候能保持行为一致。 SPIP to Standardize SQL Logical Plans 介绍了一些 high-level 的操作,并且总结了这些操作的期望行为,并期望 Spark 在内部实现上设计一种机制进行保证。这也要求 Catalog API 能对那些数据源进行创建、修改以及删除等操作。
举个例子,为了实现 CTAS,Spark 会创建、写入或者删除表(写入失败时)。这样的话,当元数据管理不可用或者 driver 自己失败的时候,CTAS 可能会删除表不成功。
除此之外,还有一个暴露 catalog API 的需求。我们使用 DataFrame 编写 Spark 程序的时候可以使用 SQL 引擎,但是并没有类似创建、修改以及删除这种 catalog 的 API 提供。在 Spark 代码中,Catalog 接口提供了一些操作,但是并不够全面和强大,比如不支持 multi catalog。
这就是 Catalog Plugin 产生的背景。
所以 Catalog Plugin 的首要目标其实是提供一组 catalog API 用来创建、修改、加载和删除表。
2. CatalogPlugin Interface
CatalogPlugin 在 Spark 代码中是一个 Interface,代码如下。
1 | /** |
从代码中我们可以获得几点有用的信息:
- 自定义 catalog 必须实现这个 interface
- 然后通过 Catalog#load(String, SQLConf) 进行加载,加载时会调用具体 Catalog 的无参构造函数方法进行初始化
- 初始化之后会调用 CatalogPlugin 中的 initialize 方法进行初始化
- 使用 CatalogPlugin 需要添加如下配置,其中第二个配置就是我们传递给 CatalogPlugin 的 initialize 方法的参数
- spark.sql.catalog.catalog-name=com.example.YourCatalogClass
- spark.sql.catalog.catalog-name.(key)=(value)
我们查看一下 CatalogPlugin Interface 的实现和继承关系可以看到如下图。我们可以看到 TableCatalog Interfact 继承了 CatalogPlugin,然后 V2SessionCatalog 和 JDBCTableCatalog 是两个具体的 class,实现了 TableCatalog。所以我们可以有理由相信 TableCatalog 中实现了创建、修改、删除表的 api。
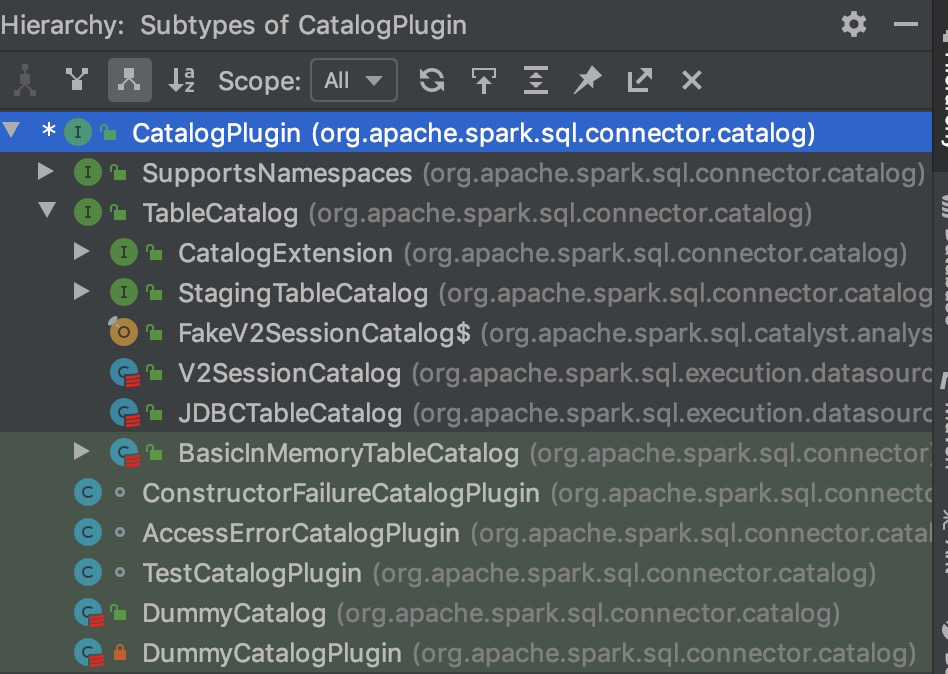
3. TableCatalog
TableConfig 也是一个 Interface,代码如下。
1 | /** |
根据注释可以看出 TableCatalog 定义了 Catalog 和表进行交互的方法,其实就是前面说的增删改。值得注意的是 TableCatalog 可以被实现成字符敏感或者字符不敏感的,实现方法是通过一个 alterTable 方法去对 field 做规范化,确实挺巧妙的。
TableCatalog 定义的方法非常的简单,都是和 table 相关的,如下,这里就不再细说的。
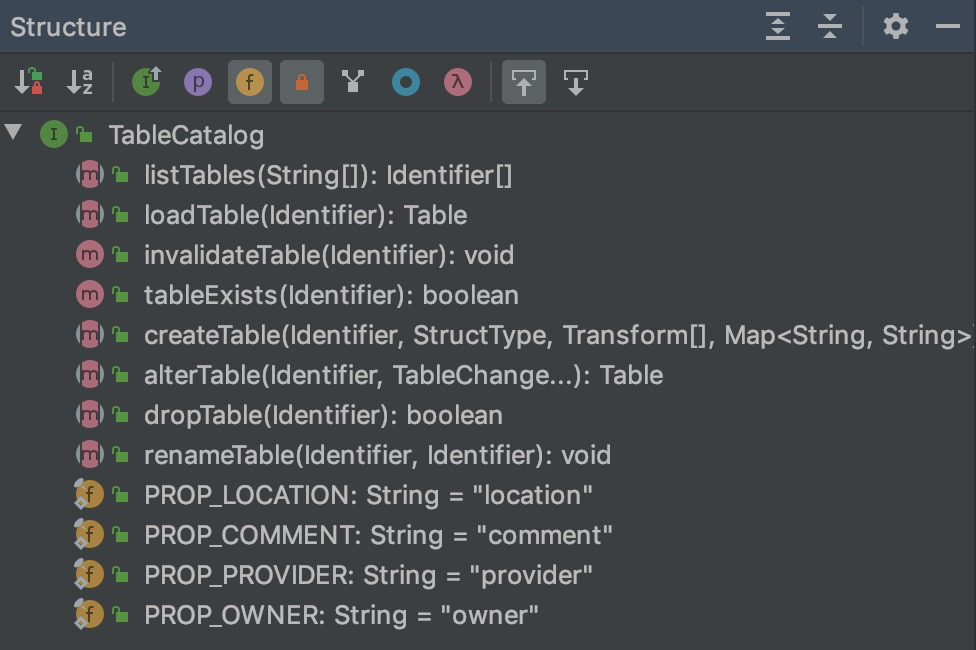
TableCatalog 的实现有 V2SessionCatalog 和 JDBCCatalog,其中 V2SessionCatalog 是为了和之前的 SparkSession 中的 Catalog 做兼容,这里就不再细说了。
4. CatalogManager
前面介绍 Catalog 使用的时候提供一个配置就可以了。
1 | spark.sql.catalog.catalog-name=com.example.YourCatalogClass |
那么我们有理由怀疑所有的 catalog 都是通过一个 Map 映射关系来管理的,实际上确实差不多,这个管理的 Class 就是 CatalogManager。
1 | /** |
从 CatalogManager 的注释中我们可以看出这就是一个 CatalogPlugin 的管理者,并且是线程安全的。我们简单看一下 CatalogManager 内部的方法和成员。
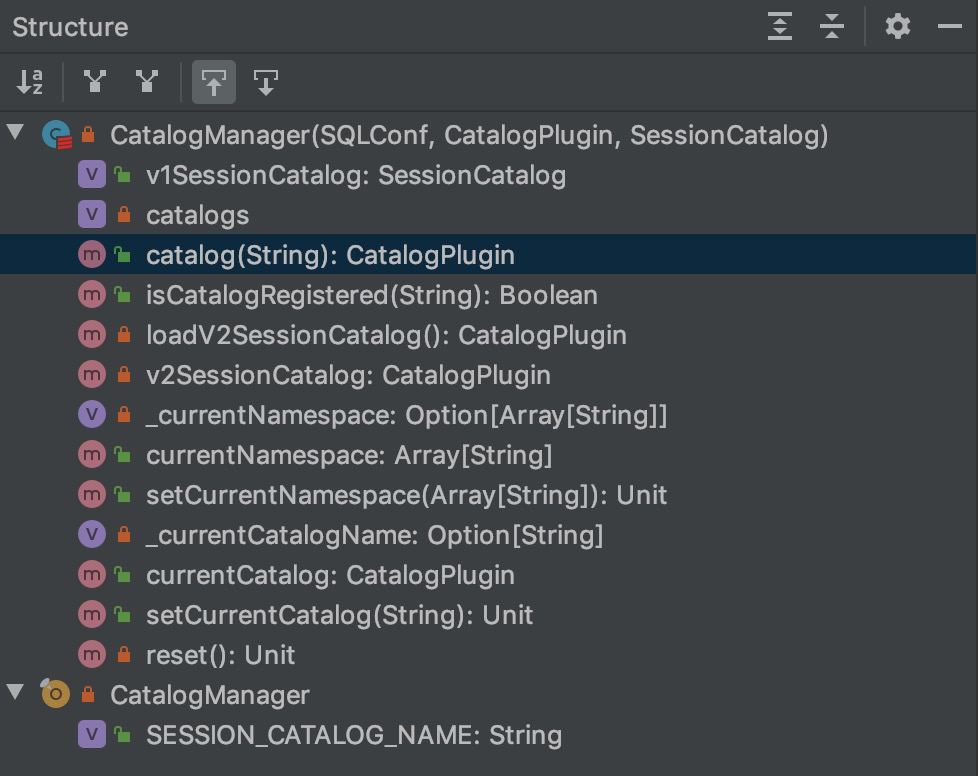
如上所示,简单介绍其中两个。
- catalogs: 一个 map: mutable.HashMap[String, CatalogPlugin],保存 catalog 名字和 Class 的隐射关系
- catalog(String):用来查找特定名字的 Catalog,返回 CatalogPlugin 接口。
5. 使用举例
使用举例下面这篇文章写的挺好的,copy 部分内容如下,全文可以移步:https://developer.aliyun.com/article/756968
基于 Spark 3.0 preview使用Iceberg + SparkSQL
在Spark DatasourceV2增加了multiple catalog等功能后,回到我们想要查询的SQL,实现步骤如下:
1.在Iceberg侧对CatalogPlugin/TableCatalog/SupportsRead等接口进行实现,实现类名如: org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog
2.在spark的配置文件中设置:
1 | spark.sql.catalog.iceberg_catalog = org.apache.iceberg.spark.SparkCatalog |
3.基于配置的catalogName,调整SQL如下,就可以进行基于SQL的跨数据源查询了。
1 | select * |
4.除了跨数据源数据分析以外,现在还可以对Iceberg的表进行DDL操作了,如,
1 | create table iceberg_catalog.t1 ...... |